By DR.TONY PHILLIPS Original here.
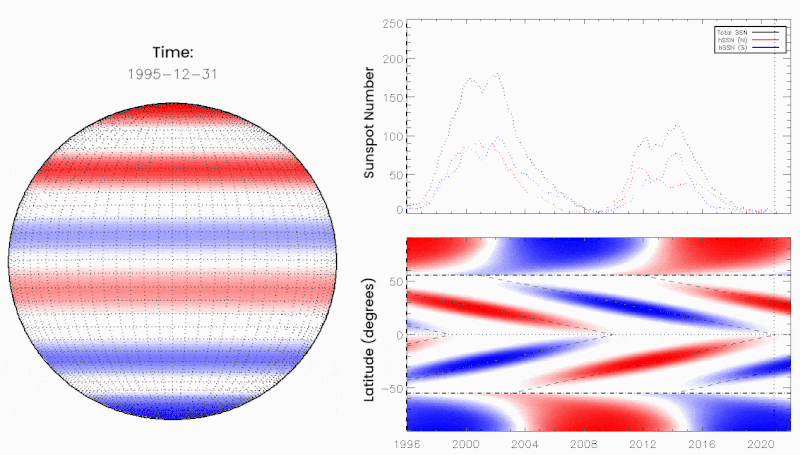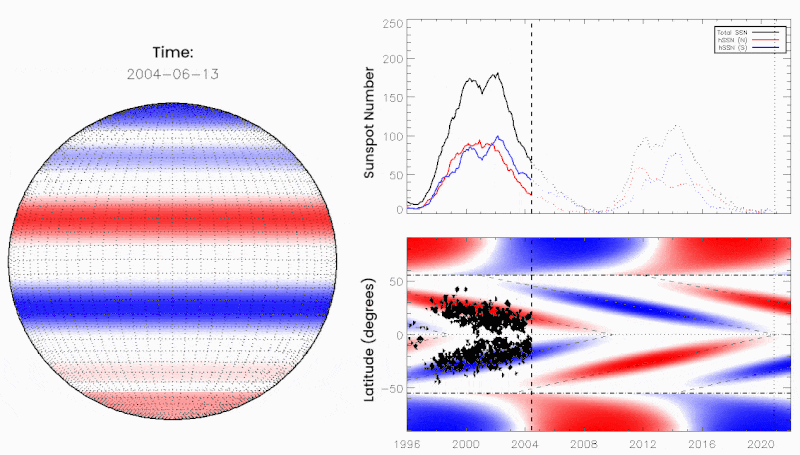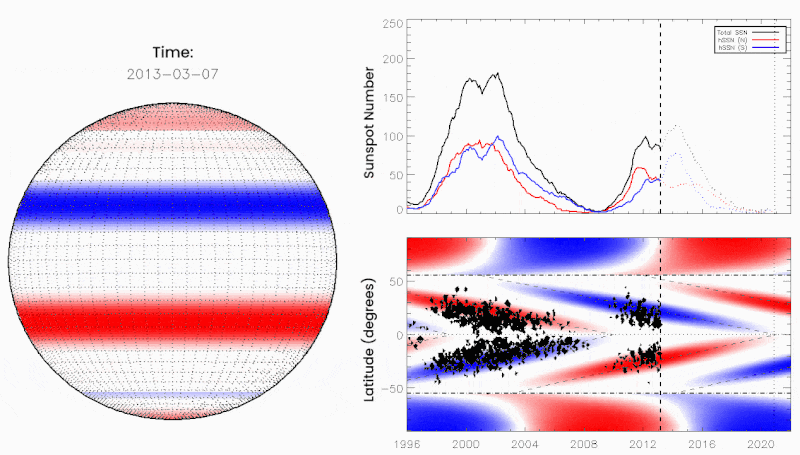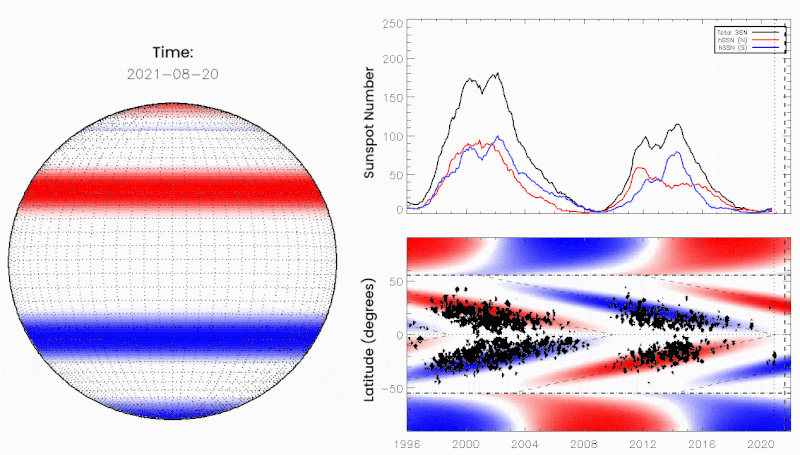
June 10, 2021: Something big may be about to happen on the sun. “We call it the Termination Event,” says Scott McIntosh, a solar physicist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), “and it’s very, very close to happening.”
If you’ve never heard of the Termination Event, you’re not alone. Many researchers have never heard of it either. It’s a relatively new idea in solar physics championed by McIntosh and colleague Bob Leamon of the University of Maryland – Baltimore County. According to the two scientists, vast bands of magnetism are drifting across the surface of the sun. When oppositely-charged bands collide at the equator, they annihilate (or “terminate”). There’s no explosion; this is magnetism, not anti-matter. Nevertheless, the Termination Event is a big deal. It can kickstart the next solar cycle into a higher gear.
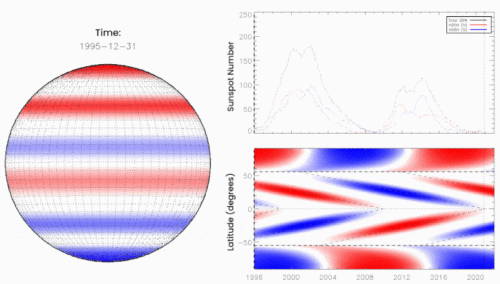
The researchers outlined their reasoning in a December 2020 paper in the research journal Solar Physics. Looking back over 270 years of sunspot data, they found that Terminator Events divide one solar cycle from the next, happening approximately every 11 years. Emphasis on approximately. The interval between terminators ranges from 10 to 15 years, and this is key to predicting the solar cycle.
“We found that the longer the time between terminators, the weaker the next cycle would be,” explains Leamon. “Conversely, the shorter the time between terminators, the stronger the next solar cycle would be.”
Abstract
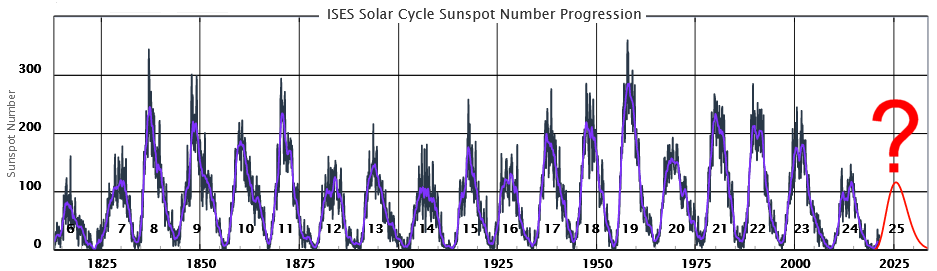
The Sun exhibits a well-observed modulation in the number of spots on its disk over a period of about 11 years. From the dawn of modern observational astronomy, sunspots have presented a challenge to understanding—their quasi-periodic variation in number, first noted 175 years ago, has stimulated community-wide interest to this day. A large number of techniques are able to explain the temporal landmarks, (geometric) shape, and amplitude of sunspot “cycles,” however, forecasting these features accurately in advance remains elusive. Recent observationally-motivated studies have illustrated a relationship between the Sun’s 22-year (Hale) magnetic cycle and the production of the sunspot cycle landmarks and patterns, but not the amplitude of the sunspot cycle. Using (discrete) Hilbert transforms on more than 270 years of (monthly) sunspot numbers we robustly identify the so-called “termination” events that mark the end of the previous 11-yr sunspot cycle, the enhancement/acceleration of the present cycle, and the end of 22-yr magnetic activity cycles. Using these we extract a relationship between the temporal spacing of terminators and the magnitude of sunspot cycles. Given this relationship and our prediction of a terminator event in 2020, we deduce that sunspot Solar Cycle 25 could have a magnitude that rivals the top few since records began. This outcome would be in stark contrast to the community consensus estimate of sunspot Solar Cycle 25 magnitude.
What does this mean?
We’re fried.
Our planet’s magnetic field is our protection from space weather, and it has been waning since 1850. This waning has increased ten-fold over recent years. If we’re about to have one of the strongest solar cycles in recorded history –as proposed by McIntosh and Leamon– then the electrical grid we modern humans rely on to survive is doomed to fail. (Electroverse.net). We have mentioned the Carrington Event (1859) before. It took out the telegraph system. Can you imagine the effect it would have today? We are bound by electricity to every aspect of our lives.
If you have never prepped before. You need to start looking at the basics. Food, water, warmth, health supplies, seeds, weapons, barterable goods. Society will respond and recover – it always does. But it could take a very long time and that time will be perilous. Look at what happened during a relatively minor event in Quebec.
The Day The Sun Brought Darkness (NASA)
On March 13, 1989 the entire province of Quebec, Canada suffered an electrical power blackout. Hundreds of blackouts occur in some part of North America every year. The Quebec Blackout was different, because this one was caused by a solar storm!
On Friday March 10, 1989 astronomers witnessed a powerful explosion on the sun. Within minutes, tangled magnetic forces on the sun had released a billion-ton cloud of gas. It was like the energy of thousands of nuclear bombs exploding at the same time. The storm cloud rushed out from the sun, straight towards Earth, at a million miles an hour. The solar flare that accompanied the outburst immediately caused short-wave radio interference, including the jamming of radio signals from Radio Free Europe into Russia. It was thought that the signals had been jammed by the Kremlin, but it was only the sun acting up!
On the evening of Monday, March 12 the vast cloud of solar plasma (a gas of electrically charged particles) finally struck Earth’s magnetic field. The violence of this ‘geomagnetic storm’ caused spectacular ‘northern lights’ that could be seen as far south as Florida and Cuba. The magnetic disturbance was incredibly intense. It actually created electrical currents in the ground beneath much of North America. Just after 2:44 a.m. on March 13, the currents found a weakness in the electrical power grid of Quebec. In less than 2 minutes, the entire Quebec power grid lost power. During the 12-hour blackout that followed, millions of people suddenly found themselves in dark office buildings and underground pedestrian tunnels, and in stalled elevators. Most people woke up to cold homes for breakfast. The blackout also closed schools and businesses, kept the Montreal Metro shut during the morning rush hour, and closed Dorval Airport.
The Quebec Blackout was by no means a local event. Some of the U.S. electrical utilities had their own cliffhanger problems to deal with. New York Power lost 150 megawatts the moment the Quebec power grid went down. The New England Power Pool lost 1,410 megawatts at about the same time. Service to 96 electrical utilities in New England was interrupted while other reserves of electrical power were brought online. Luckily, the U.S. had the power to spare at the time…but just barely. Across the United States from coast to coast, over 200 power grid problems erupted within minutes of the start of the March 13 storm. Fortunately none of these caused a blackout.
In space, some satellites actually tumbled out of control for several hours. NASA’s TDRS-1 communication satellite recorded over 250 anomalies as high-energy particles invaded the satellite’s sensitive electronics. Even the Space Shuttle Discovery was having its own mysterious problems. A sensor on one of the tanks supplying hydrogen to a fuel cell was showing unusually high pressure readings on March 13. The problem went away just as mysteriously after the solar storm subsided.
Twenty years later, the March 1989 ‘Quebec Blackout’ has reached legendary stature, at least among electrical engineers and space scientists. It is a dramatic example of how solar storms can affect us even here on the ground. Fortunately, storms as powerful as this are rather rare. It takes quite a solar wallop to cause anything like the conditions leading up to a Quebec-style blackout. Typical solar activity ‘sunspot’ cycles can produce least two or three large storms, so it really is just a matter of chance whether one will cause a blackout or not. As it is for hurricanes and tornadoes, the more we can learn about the sun’s ‘space weather,’ the better we can prepare for the next storm when it arrives!
Dr. Sten Odenwald
NASA Astronomer
ADNET/Catholic University