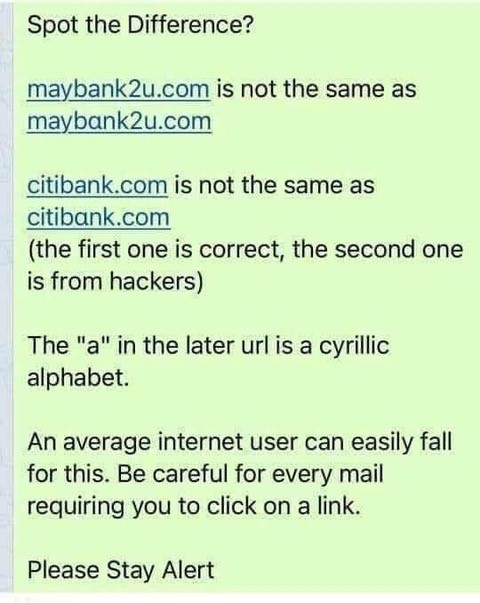
Do you know the difference between http:// and https://
The main difference between http:// and https:// is it’s all about keeping you secure.
HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol.
The “S” stands for “secure”.
If you visit a website or web page and look at the address in the web browser, it will likely begin with the following: http://
This means that the website is talking to your browser using the regular “unsecured” language.
In other words, it is possible for someone to “eavesdrop” on your computer’s conversation with the website.
If you fill out a form on the website, someone might see the information you send to that site.
This is why you never ever enter your credit card number in an http:// website!
But if the web address begins with https://,that basically means your computer is talking to the website in a secure code that no one can eavesdrop.
If a website ever asks you to enter your credit card information, you should automatically look to see if the web address begins with https://.
Again, if it doesn’t, you should NEVER enter sensitive information such as a credit card number, SIN #, etc.
How to Spot a Fake Email
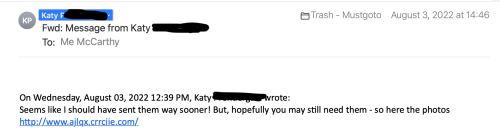
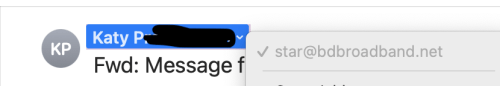
The email might say it’s from your friend Katy P. You may have had emails from her and know that her email address is [email protected]. But the message looks weird. So you click on her name and you see another email address. She has been hacked and her account is now sending spam. Delete the email. Do not open any links, forward it or reply to it. Tell Katy through a new email, or by phone or text that her account has been compromised and she should change her password.
Advice from the FTC
Scammers often update their tactics, but there are some signs that will help you recognize a phishing email or text message.
Phishing emails and text messages may look like they’re from a company you know or trust. They may look like they’re from a bank, a credit card company, a social networking site, an online payment website or app, or an online store.
Phishing emails and text messages often tell a story to trick you into clicking on a link or opening an attachment. They may
- say they’ve noticed some suspicious activity or log-in attempts
- claim there’s a problem with your account or your payment information
- say you must confirm some personal information
- include a fake invoice
- want you to click on a link to make a payment
- say you’re eligible to register for a government refund
- offer a coupon for free stuff
Here’s a real world example of a phishing email.
Imagine you saw this in your inbox. Do you see any signs that it’s a scam? Let’s take a look.
- The email looks like it’s from a company you may know and trust: Netflix. It even uses a Netflix logo and header.
- The email says your account is on hold because of a billing problem.
- The email has a generic greeting, “Hi Dear.” If you have an account with the business, it probably wouldn’t use a generic greeting like this.
- The email invites you to click on a link to update your payment details.
While, at a glance, this email might look real, it’s not. The scammers who send emails like this one do not have anything to do with the companies they pretend to be. Phishing emails can have real consequences for people who give scammers their information. And they can harm the reputation of the companies they’re spoofing.
How To Protect Yourself From Phishing Attacks
Your email spam filters may keep many phishing emails out of your inbox. But scammers are always trying to outsmart spam filters, so it’s a good idea to add extra layers of protection. Here are four steps you can take today to protect yourself from phishing attacks.
Four Steps To Protect Yourself From Phishing
1. Protect your computer by using security software. Set the software to update automatically so it can deal with any new security threats.
2. Protect your mobile phone by setting software to update automatically. These updates could give you critical protection against security threats.
3. Protect your accounts by using multi-factor authentication. Some accounts offer extra security by requiring two or more credentials to log in to your account. This is called multi-factor authentication. The additional credentials you need to log in to your account fall into two categories:
- Something you have — like a passcode you get via an authentication app or a security key.
- Something you are — like a scan of your fingerprint, your retina, or your face.
Multi-factor authentication makes it harder for scammers to log in to your accounts if they do get your username and password.
4. Protect your data by backing it up. Back up your data and make sure those backups aren’t connected to your home network. You can copy your computer files to an external hard drive or cloud storage. Back up the data on your phone, too.
What To Do if You Suspect a Phishing Attack
If you get an email or a text message that asks you to click on a link or open an attachment, answer this question: Do I have an account with the company or know the person that contacted me?
If the answer is “No,” it could be a phishing scam. Go back and review the tips in How to recognize phishing and look for signs of a phishing scam. If you see them, report the message and then delete it.
If the answer is “Yes,” contact the company using a phone number or website you know is real. Not the information in the email. Attachments and links can install harmful malware.
What To Do if You Responded to a Phishing Email
If you think a scammer has your information, like your Social Security, credit card, or bank account number, go to IdentityTheft.gov. There you’ll see the specific steps to take based on the information that you lost.
If you think you clicked on a link or opened an attachment that downloaded harmful software, update your computer’s security software. Then run a scan.
How To Report Phishing
If you got a phishing email or text message, report it. The information you give can help fight the scammers.
Step 1. If you got a phishing email, forward it to the Anti-Phishing Working Group at [email protected].
If you got a phishing text message, forward it to SPAM (7726).
Step 2. Report the phishing attack to the FTC at ReportFraud.ftc.gov.
Sometimes you just have to be very, very vigilant