Police in Georgia found a baby girl wrapped in a plastic bag on the evening of June 6. The infant …


Police in Georgia found a baby girl wrapped in a plastic bag on the evening of June 6. The infant …

One of the most preventable types of deaths from injury is uncontrolled bleeding. Learning the techniques for controlling bleeding is …
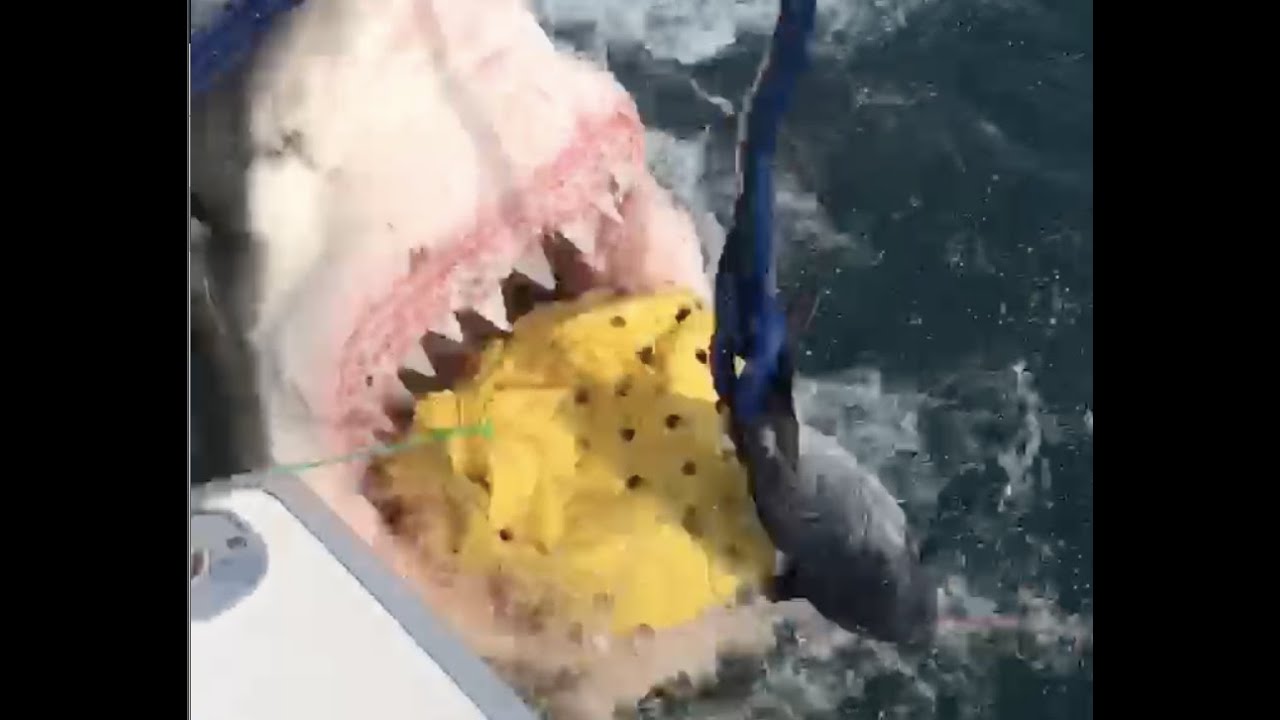

A group of New Jersey fisherman fishing got more than they bargained for when an 18-foot long, 2000-pound great white …

The American economy is booming, thanks to tax cuts and a halt to the Obama onslaught of regulations. But two …

A Missouri police officer wounded and taken hostage when an inmate snatched her weapon was saved when an armed citizen …
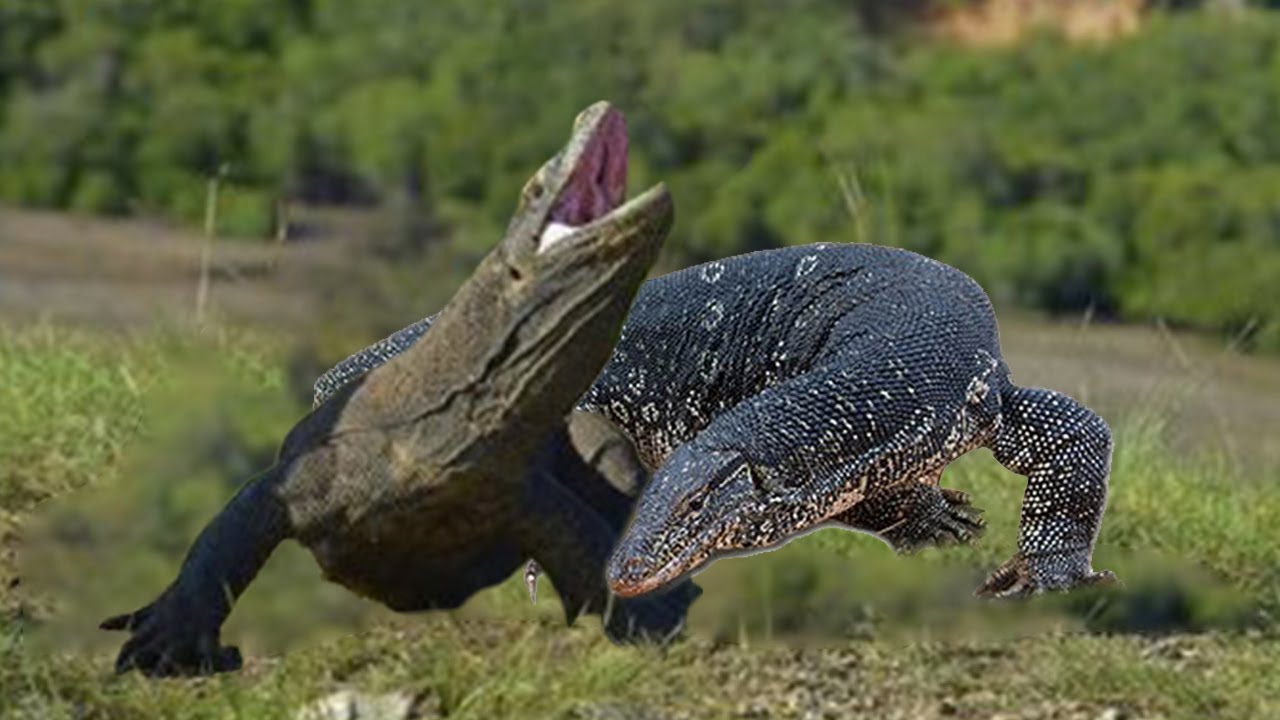

Watch these two massive monitor lizards go head to head in a battle for dominance. They are huge and for …

Australian researchers have found odd bone spurs growing out of the skulls of young people. These “horns” are said to …
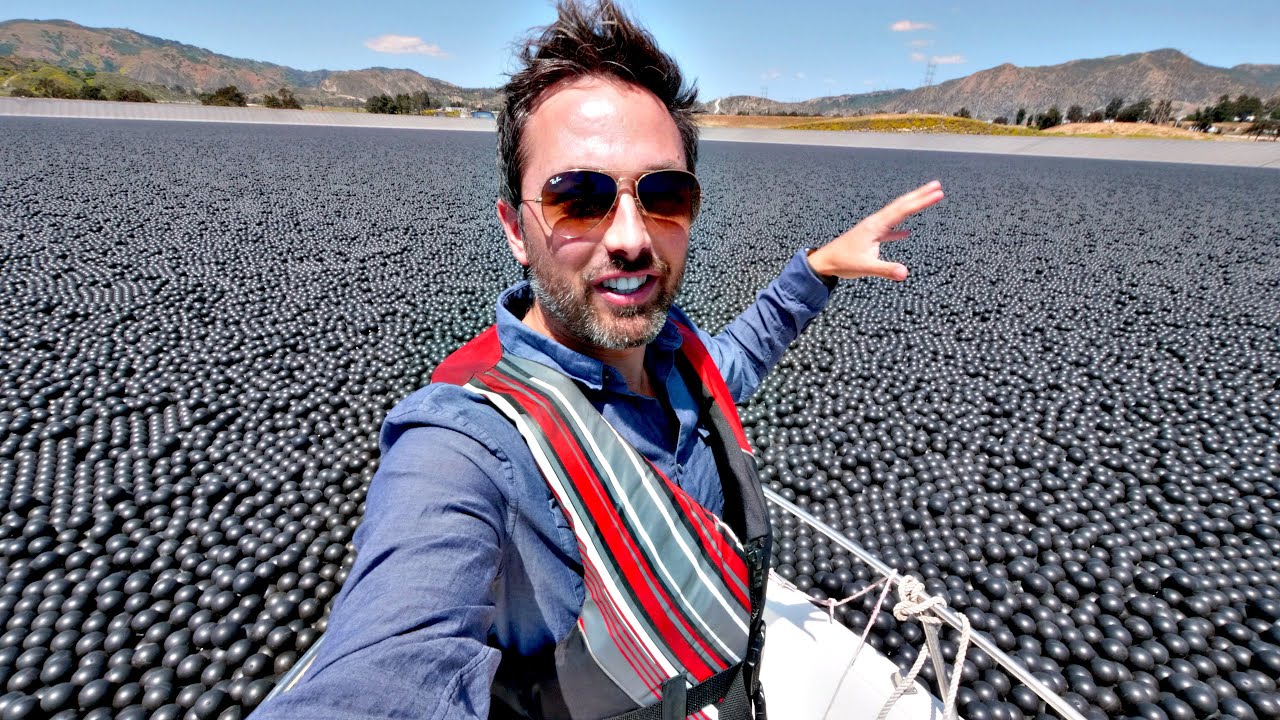

It looks like the world’s biggest ball pit. But it’s actually a very ingenious way the L.A. water authority discovered …

Facebook is getting into the cryptocurrency game, embracing a technology that allows people to engage in voluntary transactions outside the …
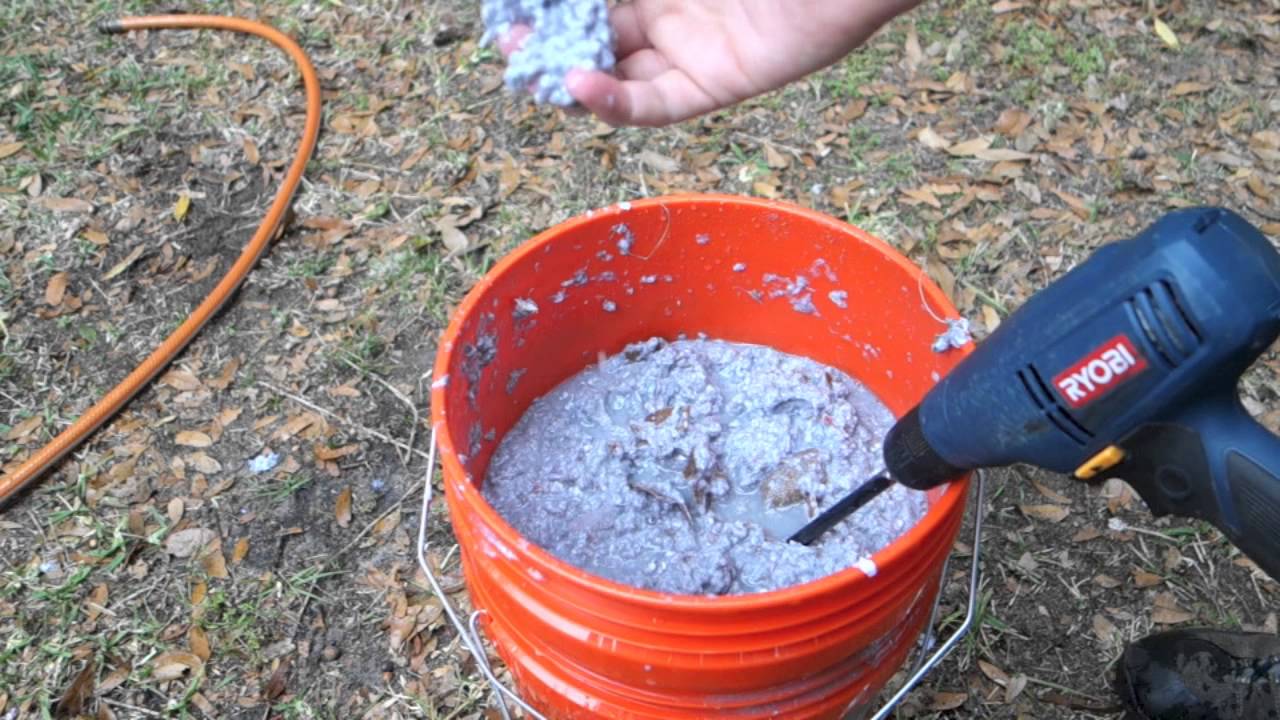

Most of us have a steady supply of waste paper which ends up in recycle bins or your garbage can. …
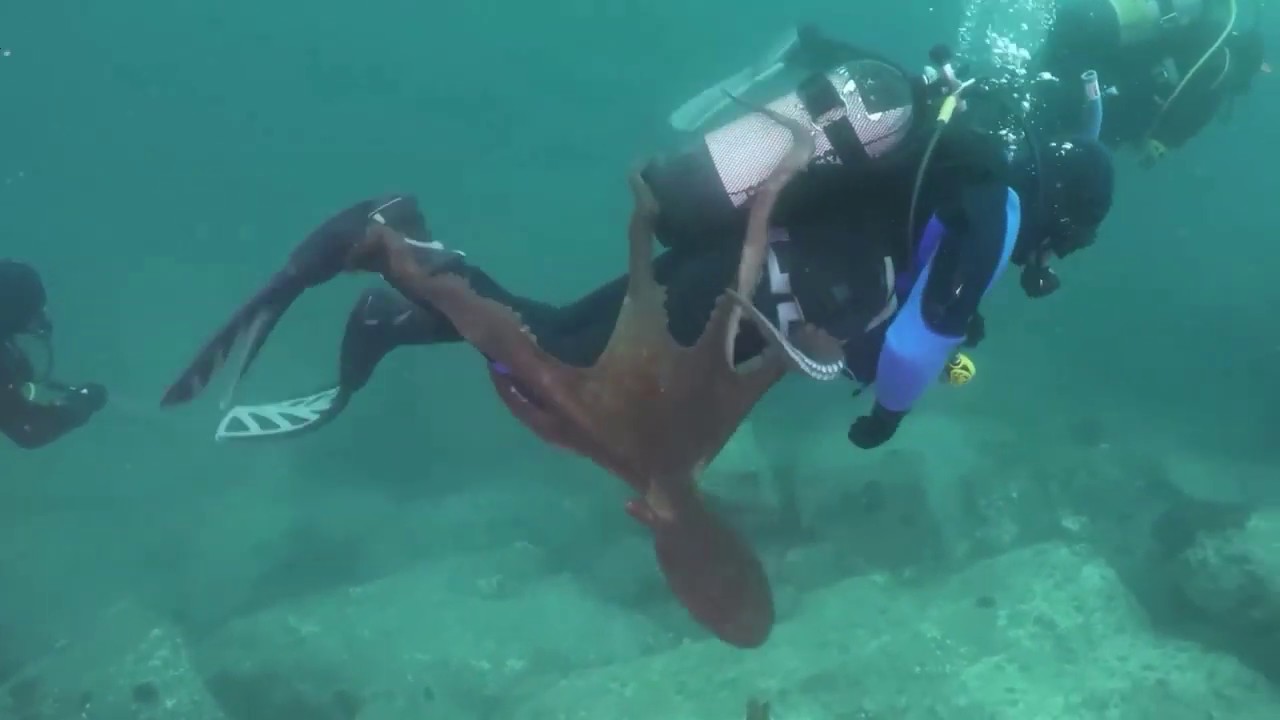

Watch this octopus as it encounters a group of divers in the Japanese Sea earlier this month. Is it being …
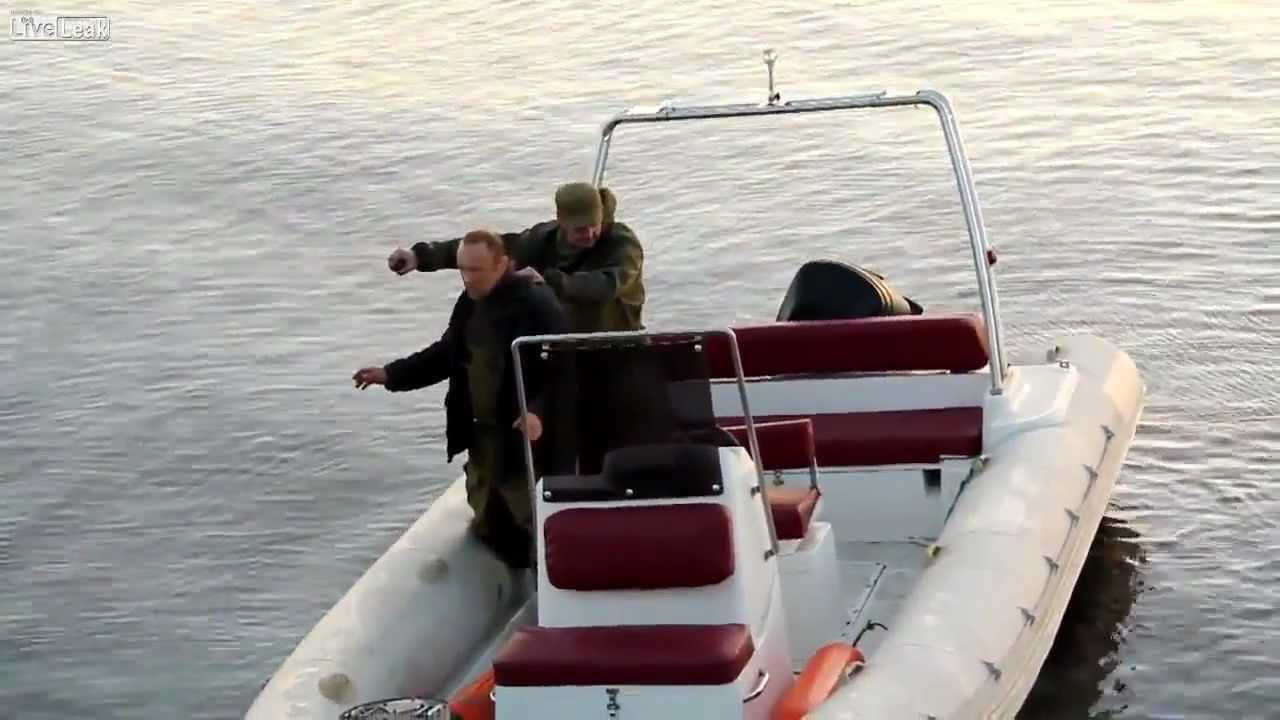

Dear Lord, some people are specially dumb! These Russians decide to look cool and drop a grenade off the side …
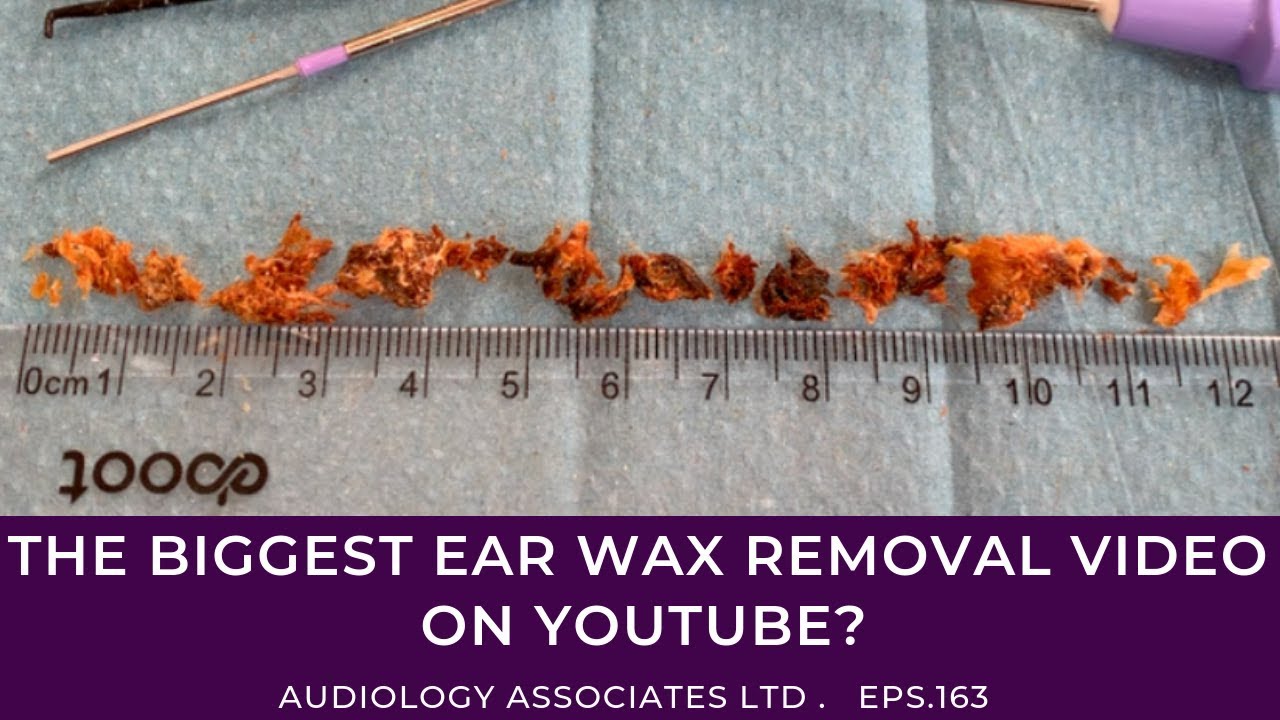
This is so gross, but it’s a great lesson that ear hygiene is important. This build up is being removed …

The truth is unavoidable: Social Security is insolvent. It’s set to run out of money to pay scheduled benefits in …

(Natural News) In trying to come up with a plan for when everything hits the fan, many folks end up stumbling …

Contrary to the rhetoric of many gun control advocates, the Second Amendment’s protection of the individual right to keep and …

No that is not a Mad Libs headline. Officers in Alabama discovered a drug dealer who fed meth to a …
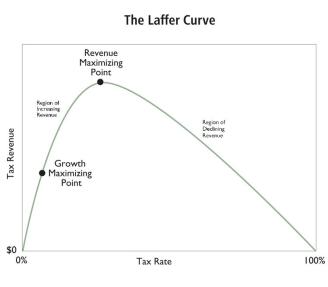
On June 19th, President Trump awarded economist Art Laffer, creator of the Laffer Curve made famous under President Reagan, the …

IRS agents have been stealing cash from taxpayers for years, sometimes hundreds of thousands of dollars at time, and it’s …
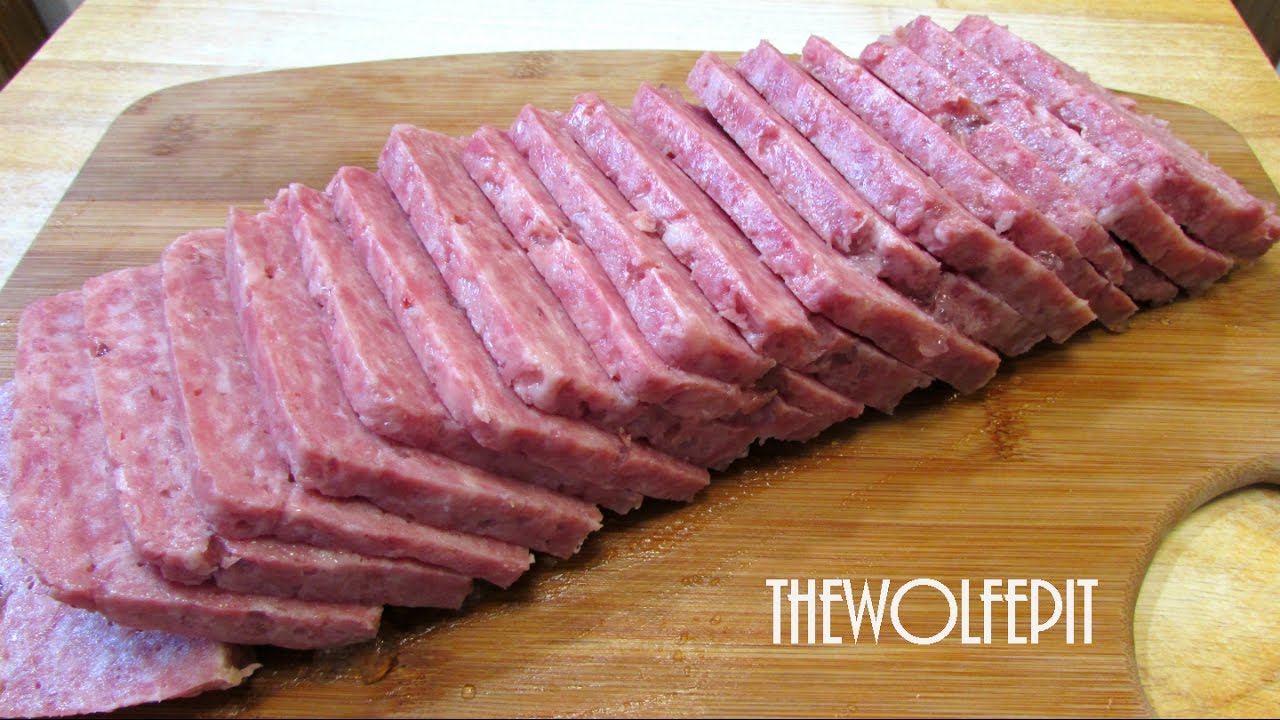

It’s the ultimate survival food. It powered our troops in World War II and decades-old cans are still edible. And …
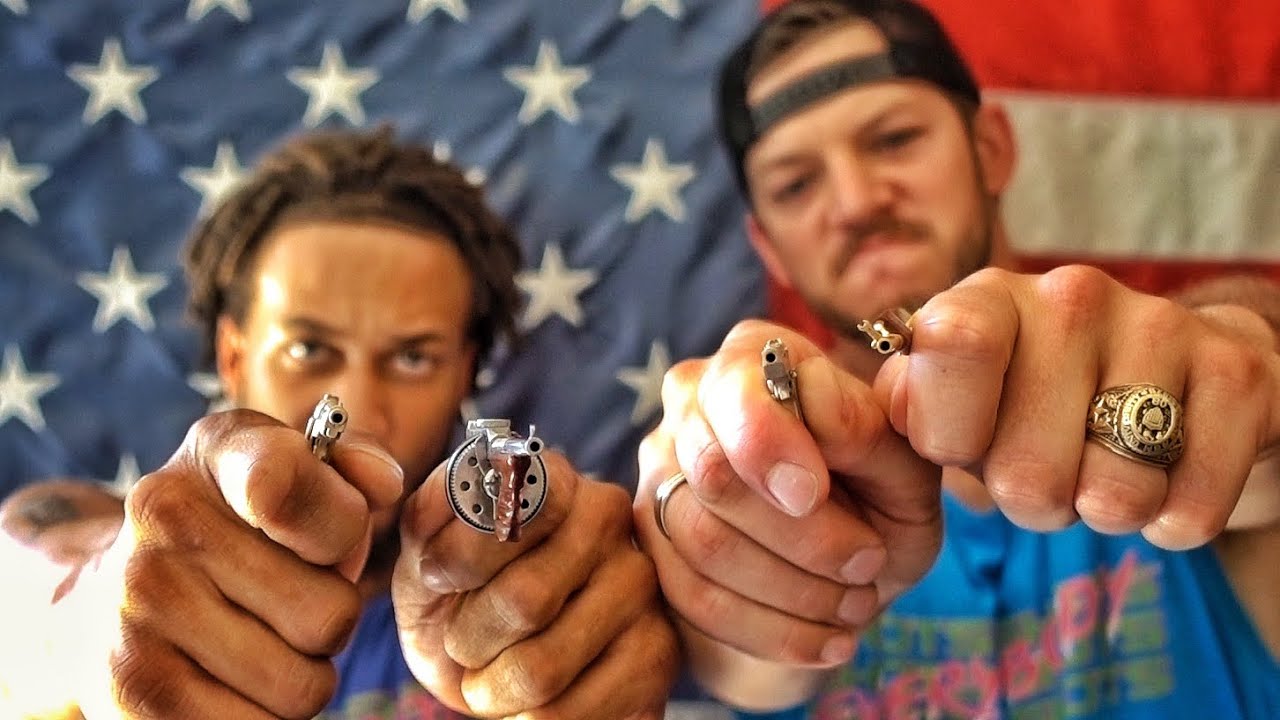

Is bigger always better? Check out these super tiny WORKING firearms. A desert eagle, a tommy gun and a tiny …

While some people invest in precious metals as an investment, preppers tend to look at is as a useful currency …
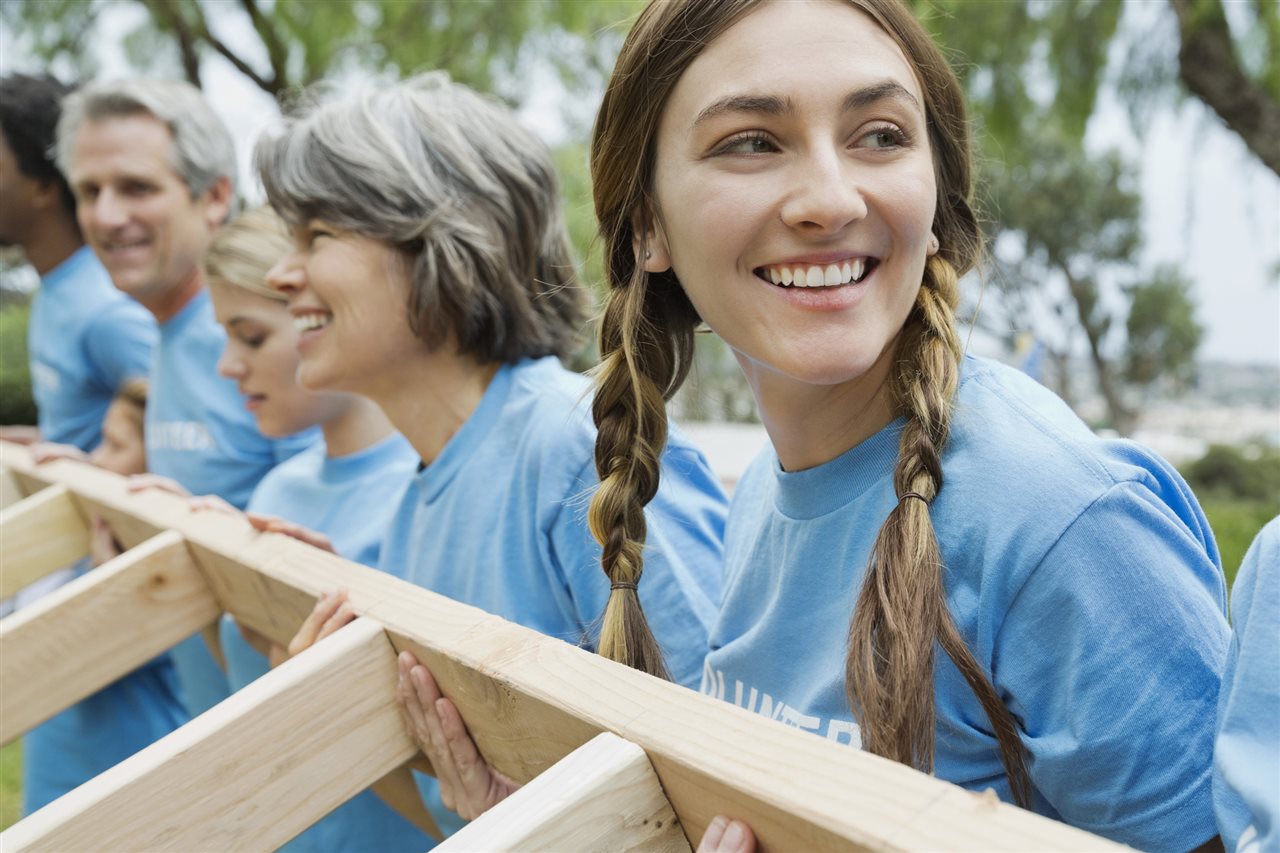

(BPT) – Looking for a vacation that’s fun and meaningful? Wish you had more time to volunteer in a way …
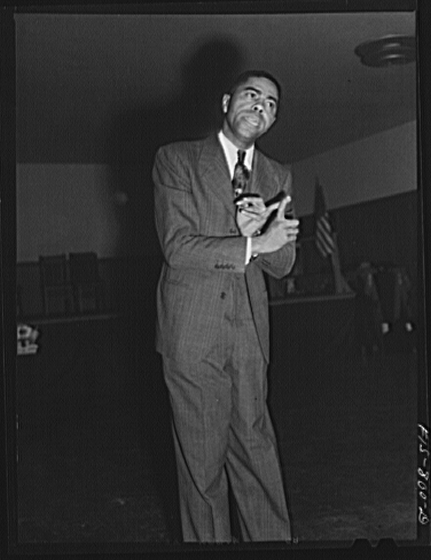

In the days before President Lyndon Baines Johnson, black Republicans were a thing. And chief among them was Samuel B. Fuller. Fuller …
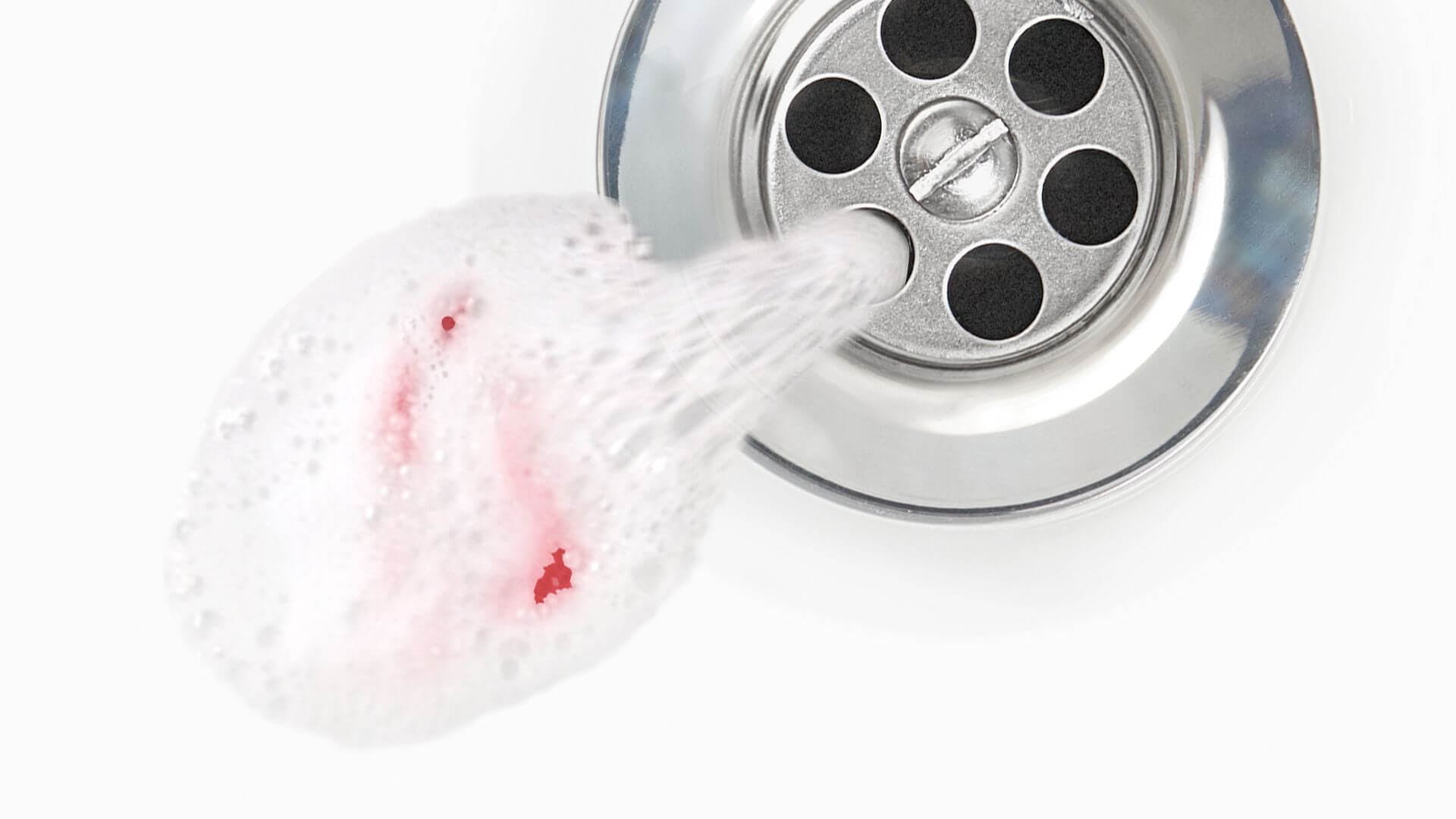

Porphyromonas Gingivalis is the key bacteria that leads to chronic gum disease. This can cause your gums to bleed so …

Did you know you can start a fire with water? You’re stranded. You know it could be a while until …

A central Texas wheat farmer, an Austin distillery and Texas A&M geneticists are teaming up to produce whisky from 100-year …

Watch as this massive icebreaker cuts through the thick polar icepack and try to imagine what it would be like …

Usually, we host videos showing snakes eating any number of creatures. So this time, let’s take a look at how …

Scientists are warning that a solar superflare on the sun could take Earth’s power systems offline sooner than previously thought. …